You can improve workplace productivity and save your company money by incorporating our automatic, semi-automatic, or manual tape dispensers into your existing production lines. Our dispensers are available with liner take-up attachments, deliver either random or definite lengths, and work with many different types of tape. Below, we have provided information about different types of tape and the construction of tape.
Explore our tape dispensers here.
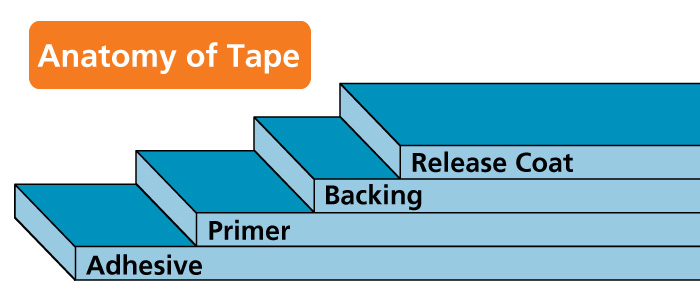
Adhesive
The adhesive system used is as important as the backing. The two must be compatible.
Adhesives must withstand the solvents in commonly used varnishes and resins. Raw materials and the manufacturing process must be controlled to make sure that no corrosive elements, such as sulfur and chlorides, are present.
Primer
A priming layer is sometimes placed between the adhesive and the backing. Without it, the adhesive would adhere to either surface of the backing indiscriminately. The primer is designed to prevent adhesive transfer. As with the adhesive, the priming layer must be electrical grade and solvent resistant.
Backing
The backing is the layer that insulates, protects or holds electrical and electronic devices. Common backings are glass cloth, polyester, PTFE, Dysular Film, polyimide and composites. The properties of the backing can often be improved by special treatments.
Release Coat
Most electrical tapes have an electrical grade release coat or “easy unwind” treatment applied to the tape backing. It assures smooth unwind for hand and machine dispensing: The treatment must be compatible with the backing and provide an acceptable measure of adhesion so that the tape will not end lift if it is wrapped back on itself in application. The release coat is critical in assuring good shelf life and a stable, easy-to-use roll of tape.
Examples of Backings
See selected examples of machine compatibility underneath each description.
Dysular Film
This thin film offers excellent conformability for easy application, high dielectric strength, moisture and solvent resistance and printability. The versatility of this backing results in material and labor cost savings when used instead of low performance polyester film tapes.
See the TDA080-NM..
Epoxy Film
This versatile tape offers solder and puncture resistance, thinness, high dielectric strength and conformability and can be used for a wide variety of applications.
See the zcM1000T.
Composite Film
This construction combines the high dielectric strength and edge-tear resistance of polyester film with the cushioning properties of nonwoven polyester mat. It is available in five thicknesses. It is an alternative to polyester/paper tapes in many applications, due to its temperature rating, superior puncture resistance and flexibility.
See the zcM1000T.
Polyester Film
These tapes are specified for insulation applications requiring a thin, physically durable and high dielectric strength tape that can withstand higher temperatures. Polyester tapes are conformable, exhibit excellent chemical, solvent and moisture resistance and resist cut-through and abrasion.
See the TDA080 & zcM1000.
PPS Film
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) film tapes meet the demands of space limitations in high temperature applications such as motors, coils, transformers and capacitors.
See the TDA080-NM.
Polyimide Film
Tapes with polyimide backing can be used in applications such as coils, harnesses and capacitors that undergo extreme temperature variations. Under such conditions, these tapes’ physical and electrical properties remain stable.
See the zcM1000K or zcM1000B.
Glass Cloth
These tapes offer the most flexible and conformable glass cloth backings on the market. They also have the highest temperature resistance and tensile strength among woven products and offer excellent absorption of electrical insulating resins and varnishes. Scotch glass cloth tapes are unsurpassed for banding and strapping applications.
See the zcM1000C.
Acetate Cloth
These aesthetically pleasing, coil-covering tapes offer excellent conformability and absorption of resins and varnishes.
See the TDA080 or zcM1000C.
Cotton Cloth
This tape offers outstanding abrasion resistance and toughness for heavy-duty, 105°C applications and is very compatible with electrical insulating resins and varnishes.
See the TDA080 or zcM1000C.
Filament Reinforced
These tapes were designed for applications where both the dielectric strength of polyester film and the high mechanical strength of glass cloth are required. Offering the ultimate in low stretch, high tensile strength and edge-tear resistance, these products are more cost effective than glass cloth tapes.
See the zcM1000, TDA080, zcM1000NS and TDA080-NS.
Paper
These tapes provide good cushioning, puncture resistance, and toughness. Their crepe and fiber backing materials are highly conformable and provide aesthetically pleasing coil coverings.
See the TDA080 or zcM1000.
PTFE Film
These high temperature film tapes are used in applications requiring consistent performance and minimum shrinkage across a wide range of temperatures. They are extremely resistant to chemicals, have high arc resistance and are free of carbonizing materials.
See the TDA080 or zcM1000.
Foil
Foil tapes satisfy most requirements for effective grounding, bonding, and EMI shielding at costs well below other shielding and connecting methods. They are available with aluminum, copper and tin-alloy-coated copper backings (both smooth and embossed) and with conductive and nonconductive adhesive systems.
See the zcM1000NM and TDA080-NM.
Examples of Adhesives
RT (Rubber Thermosetting)
Thermosetting adhesives have good initial adhesion and electrical purity. When subjected to the recommended thermosetting cycle, a rubber-resin adhesive system will crosslink into a three-dimensional matrix molecular form providing greater adhesion and bonding, higher solvent resistance and higher heat resistance.
A (Acrylic)
Acrylic adhesives are synthetic polymers that have been specifically formulated by 3M to meet the individual needs of the applications for which the tapes were designed. Acrylic adhesives are compounded for good resistance to heat,oxidation, solvents and oils.
ST (Silicone Thermosetting)
Silicone adhesive systems are compounded in a manner similar to that used for rubber-resin systems. However, the thermosetting reaction requires considerably higher temperatures. A silicone adhesive system has exceptional heat resistance, is inorganic and, if burned, leaves a nonconductive residue. It may be applied at very low temperatures.
Non-thermosetting Adhesives RN and AN
An adhesive system is classified as non-thermosetting if it does not advance in cure upon application of heat.
Resource: EIS Inc.